[ad_1]
At Microsoft Ignite, Microsoft introduced an AI assistant for Azure troubleshooting and more. Azure now hosts NVIDIA generative AI foundation models.
Microsoft’s generative AI assistant Copilot is now available in limited preview for IT teams using Azure, the company announced today during the Microsoft Ignite conference. Microsoft expects to expand Copilot for Azure to the Azure mobile app and the Azure command line interface at an unspecified time in the future.
During Microsoft Ignite, generative AI foundation model services from NVIDIA were also announced. NVIDIA AI foundation models are available wherever NVIDIA AI Enterprise is offered globally. Microsoft Copilot for Azure is available wherever the Azure portal can run in the public cloud.
Jump to:
Copilot comes to Microsoft Azure for IT management
IT teams can use Copilot within Microsoft Azure (Figure A) to manage cloud infrastructure. Copilot will use the same data and interfaces as Microsoft Azure’s management tools, as well as the same policy, governance and role-based access controls.
Figure A
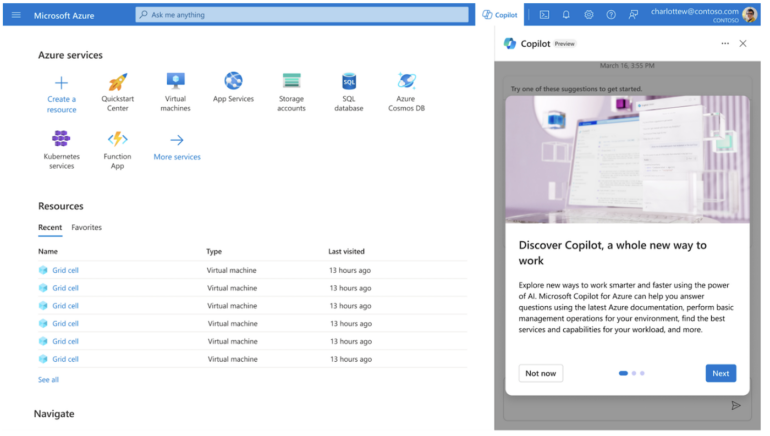
Copilot for Azure can:
- Assist with designing and configuring services.
- Answer questions.
- Author commands.
- Troubleshoot problems by using data orchestrated from across Azure services.
- Provide recommendations for optimizing an IT environment in terms of spending.
- Answer questions about sprawling cloud environments.
- Construct Kusto Query Language queries for use within Azure Resource Graph.
- Write Azure command line interface scripts.
Generative AI foundation model service added to Microsoft Azure
NVIDIA AI foundation models for enterprise can now be run on Microsoft Azure, speeding up the creation and runtime of generative AI, NVIDIA announced on Nov. 15. Models including Llama 2 and Stable Diffusion can be accessed through NVIDIA’s AI Foundation Endpoints.
Every enterprise company using this service will have its own data warehouses, which are accessed through retrieval-augmented generation. Instead of writing SQL queries to connect to existing data warehouses, retrieval-augmented generation accesses data via an embedding model. Embedding stores the semantic representation of content as a vector in a vector database. When an employee searches that database, the query is converted to embedded form and searches for vector databases to find the closest semantically-linked content. Then, a large language model uses that content as a prompt to produce a curated response.
“It’s the same workflow of using a LLM to produce responses and answers, but it is now leveraging the enterprise data warehouse of an enterprise company to produce the right answers that are topical and up to date,” said Manuvir Das, vice president of enterprise computing at NVIDIA, during a prebriefing on Nov. 14 prior to the start of Microsoft Ignite.
All of the hardware and software for an end-to-end enterprise generative AI workflow are now running on Microsoft Azure, NVIDIA announced.
“What makes this use case so powerful is that no matter what industry and enterprise company is in, and no matter what job function a particular employee at that company may be in, generative AI can be used to make that employee more productive,” Das said during the prebriefing.
SEE: See how Microsoft Azure stacks up to rival enterprise cloud computing service Google Cloud. (TechRepublic)
Developers will be able to run generative AI based on NVIDIA’s new family of NeMo Megatron-LM 3 models and more on a browser with the NVIDIA AI foundation models service. NVIDIA plans to keep up an aggressive release cadence with generative AI products and platforms, Das said, and the company is planning to release larger models of NeMo, up to hundreds of billions of parameters.
The foundation model service allows developers access to community AI models such as Llama 2, Stable Diffusion XL and Mistral. NVIDIA AI foundation models are freely available on the NVIDIA NGC catalog, Hugging Face and the Microsoft Azure model catalog.
More NVIDIA news from Microsoft Ignite
Tensor RT-LLM v0.6 will be available on Windows, providing faster inference and added developer tools for local AI on NVIDIA RTX devices. Stable Diffusion, Megatron-LM and other generative AI models can be executed locally on a Windows device, Das said.
This is part of NVIDIA’s endeavor to take advantage of generative AI capabilities on client devices that have GPUs, Das said. For example, a TensorRT-LLM-powered coding assistant in VS Code could use the local Tensor RT-LLM wrapper for OpenAI Chat API in the Continue.dev plugin to reach the local LLM instead of OpenAI’s cloud and therefore provide a developer an answer to their query faster.
In addition, NVIDIA announced new capabilities for automotive manufacturers in the form of Omniverse Cloud Services on Microsoft Azure, which creates virtual factory plans and autonomous vehicle simulation for the automotive industry.
[ad_2]